 THE FDA APPROVED WEEKLY INJECTION FOR WEIGHT LOSS
THE FDA APPROVED WEEKLY INJECTION FOR WEIGHT LOSS
Semaglutide is a once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) injection. This medication improves glycemic control and delays gastric emptying. This results in decreased appetite, reduction of food cravings, and improved control of eating. This peptide is well studied and is successful at decreasing HbA1c in those with diabetes and is associated with weight loss.
What Is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide belongs to a class of medications initially used to treat diabetes by mimicking a natural hormone (GLP-1) that prompts the body to produce more insulin after eating. That, in turn, reduces blood sugar levels and impacting the areas of the brain that regulate food intake and appetite; therefore reducing your appetite and feelings of hunger. And yes, these drugs often come with the bonus side effect of weight loss. Other prescription weight loss medications on the market that act on the central nervous system to suppress appetite (though by a different mechanism than GLP-1 drugs) include bupropion-naltrexone (Contrave) and phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia). None of these other drugs come close to the efficacy of semaglutide, according to experts and published studies.
What Does Semaglutide Do to Your Body?
Semaglutide helps to keep your blood sugar low, to allow fat burning to happen while also slowing gastric emptying to aid in appetite control and keep you feeling fuller longer. Semaglutide is in a class of medicines called incretin mimetics which work by helping the pancreas to correctly release insulin when blood sugar levels are high. Insulin helps move glucose from the blood into the tissue around the body, which is then used for energy.
Is Semaglutide Good for Weight Loss?
According to the CDC, 73% of American adults are overweight or obese. Being overweight or obese is a serious health risk associated with health conditions such as stroke, heart disease, and diabetes. Plus, it’s linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer. Losing 5-10% of body weight through diet and increased physical activity lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease in obese and overweight adults. Recent research has shown that semaglutide is an effective treatment for weight loss
How do I take Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is taken in a weekly injection. The injection is administered in the abdomen, thigh, or arm.
What doses of Semaglutide are available?
In order to not experience side effects by taking higher doses, Semaglutide is intended to be titrated in increases doses each month. Our titration schedule is most similar to that of Wegovy.
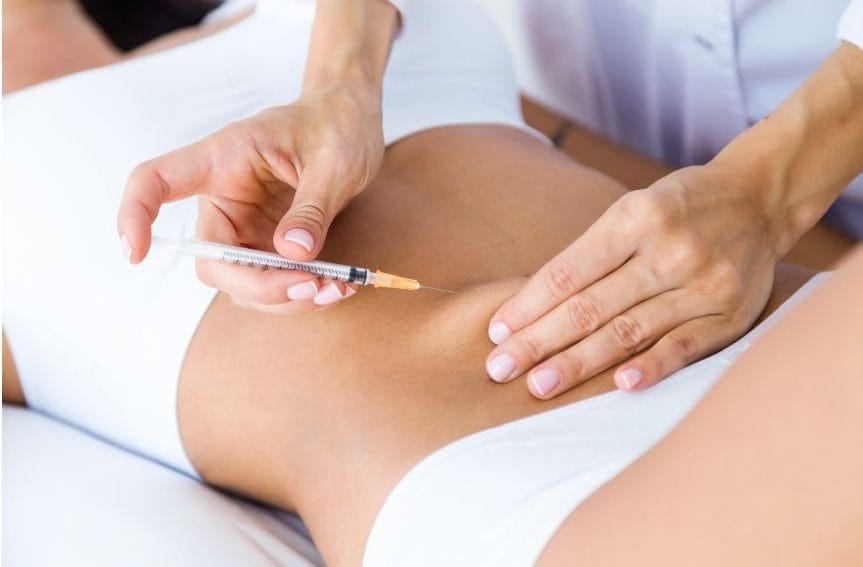
Semaglutide Injection
Month 1: 0.25 mg Semaglutide + Cyanocobalamin 0.5 mg (1mg/1mL vial – 4 doses)
Month 2: 0.5 mg Semaglutide + Cyanocobalamin 0.5 mg (1mg/2.5mL vial – 5 doses)
Month 3: 1 mg Semaglutide + Cyanocobalamin 0.5 mg (5mg/1mL vial – 5 doses)
Month 4: 1.7 mg Semaglutide + Cyanocobalamin 0.5 mg (5mg/2.5mL vial – 7 doses)
Month 5: 2.4 mg Semaglutide + Cyanocobalamin 0.5 mg (5mg/2.5mL vial – 5 doses)
Semaglutide Side Effects
The most commonly reported side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and constipation. The risk of serious side effects increases in patients with hypoglycemia, kidney problems, and risk of allergic reactions. In addition, vitamin B12 has been shown to assist with the tolerance of semaglutide and can ease some of the gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea and hypophagia.
Contraindications
Semaglutide injections shouldn’t be combined with other GLP-1 receptor agonists such as rybelsus, bydureon, trulicity, or Victoza. In addition, semaglutide should not be used in patients with a family or personal history of medullary thyroid cancer or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 (MEN 2)
 THE FDA APPROVED WEEKLY INJECTION FOR WEIGHT LOSS
THE FDA APPROVED WEEKLY INJECTION FOR WEIGHT LOSS